Running blender with the argument “-W” starts it in fullscreen mode.
But under OSX, users applications stored in the folder /Applications are not ran like command line tools.
In a terminal windows, using CLI, you are supposed to run the command open to invoke users applications.
Then, you can add an argument to open to append arguments to your executable!
open /Applications/Blender/blender.app --args -W
I tried to put it directly in Info.plist which wasn’t possible.
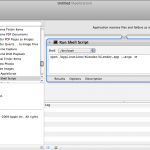
Using automator I have been able to build another user application (kind of script) that runs Blender with the fullscreen parameter.
All through the Finder so it’s easy, even for newbs and lazy creatures.
Finally you can shortcut it to your dock or anywhere else.
ERRATA
I had some strange issues using the -W switch. Use the command below instead :
open /Applications/Blender/blender.app --args -p 0 900 1440 900
Where 1440 and 900 are X & Y of your resolution.
Open the package using open package content of your Automator script and edit Info.plist. Add:
<key>LSUIPresentationMode</key> <real>4</real>
/ERRATA